ICS & SCADA OPERATIONAL EXELLENC
- Essential frameworks enabling centralized monitoring and management of vast and complex industrial operations.
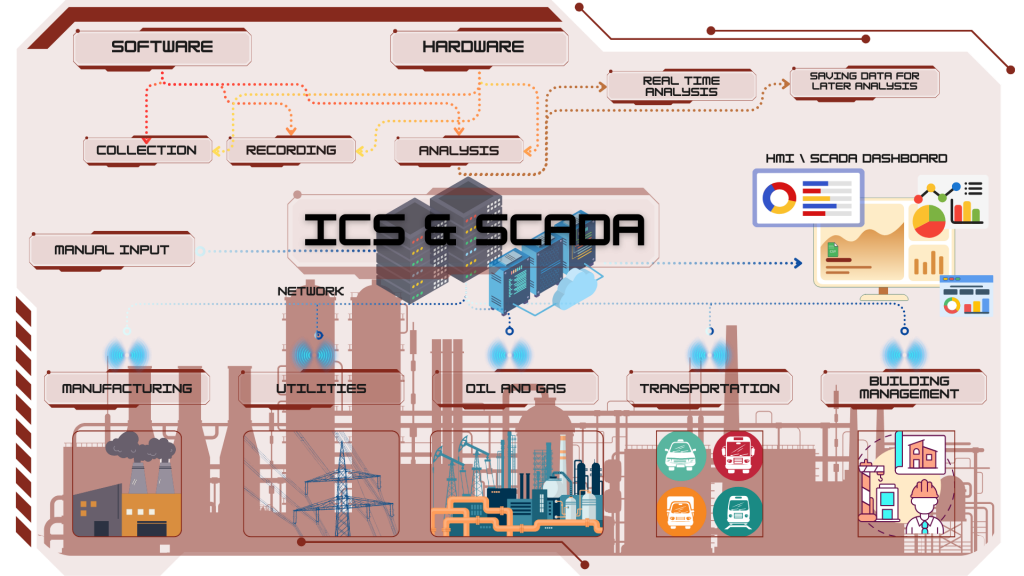


monitor, control, and automate processes
- Bridging the divide between digital technology and physical machinery, these systems make large-scale production both efficient and insightful.
Key Benefits of ICS

Automation
Reduces the need for manual intervention, improving efficiency and consistency.

Real-Time Monitoring
Provides instant feedback on process performance, enabling quick adjustments.

Improved Safety
Monitors critical parameters to prevent hazardous conditions and ensure safe operations.

Data Collection & Analysis
Gathers data for trend analysis, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.

Cost Savings
Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, leading to cost reductions.

Step 1: Data Acquisition
- Sensors and Field Devices: SCADA systems begin by collecting data from various sensors and field devices located throughout the industrial process. These sensors measure parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow rates, and other critical variables.
- Data Transmission: The collected data is transmitted from the sensors to the SCADA system using communication protocols. This transmission can be wired or wireless, depending on the setup.
Step 2: Data Communication
- Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): The transmitted data is received by RTUs and PLCs. These devices play a crucial role in aggregating the data from the sensors and preparing it for further processing.
- Network Communication: RTUs and PLCs communicate the aggregated data to the central SCADA system via a secure and reliable network. This network can be a local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN), or even the internet.
Step 3: Data Processing and Visualization
- SCADA Software: The central SCADA system, equipped with specialized software, processes the incoming data. This involves filtering, analyzing, and converting the raw data into meaningful information.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): The processed data is then displayed on HMIs. These interfaces present the data in the form of graphs, charts, and real-time metrics, making it easy for operators to monitor the system's performance and status.
Step 4: Control and Automation
- Real-Time Monitoring: Operators continuously monitor the data displayed on the HMIs to ensure that the industrial process is running smoothly. Any anomalies or deviations from the expected parameters trigger alerts and alarms.
- Automated Control: Based on the real-time data and predefined control logic, the SCADA system can automatically adjust processes to maintain optimal performance. For example, if a temperature sensor detects a high reading, the SCADA system can automatically adjust the cooling mechanism to bring the temperature back to the desired range.
- Automated Control: Based on the real-time data and predefined control logic, the SCADA system can automatically adjust processes to maintain optimal performance. For example, if a temperature sensor detects a high reading, the SCADA system can automatically adjust the cooling mechanism to bring the temperature back to the desired range.
Applications of ICS

Manufacturing
Automation of production lines, quality control, and process optimization.

Utility
Management of electrical grids, power generation, and distribution systems.

Transportation
Control of water treatment plants, distribution networks, and sewage systems.

Oil and Gas
Monitoring and control of drilling operations, pipeline management, and refinery processes.

Building Management
Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, leading to cost reductions.
Contact Us Today and Find Out More!
© All Rights Reserved.